Germany to host Europe's first exascale supercomputer
Germany will be the host of the first publicly known European exascale supercomputer, along with four other EU sites getting smaller but still powerful systems, the European High Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC JU) announced this week.

Germany will be the home of Jupiter, the "Joint Undertaking Pioneer for Innovative and Transformative Exascale Research." It should be switched on next year in a specially designed building on the campus of the Forschungszentrum Jülich research centre and operated by the Jülich Supercomputing Centre (JSC), alongside the existing Juwels and Jureca supercomputers.
The four mid-range systems are: Daedalus, hosted by the National Infrastructures for Research and Technology in Greece; Levente at the Governmental Agency for IT Development in Hungary; Caspir at the National University of Ireland Galway in Ireland; and EHPCPL at the Academic Computer Centre CYFRONET in Poland.
According to EuroHPC, Jupiter will be used to help solve important scientific problems such as climate change, how to combat pandemics and sustainable energy production. It is also intended to enable applications involving artificial intelligence and the analysis of large data volumes.
Achieving the level of exascale is the next big step in the field of high performance computing, said Professor Dr Astrid Lambrecht, of the Forschungszentrum Jülich board of directors.
"Our aim is to offer the most powerful infrastructure in Europe that combines neuromorphic computing, supercomputing, and quantum computing, ensuring that various user groups from science and industry can learn and grow together while also benefiting from each other," she said.
Half of the €500 million (about $520 million, or £430 million) funding for Jupiter is coming from the EuroHPC JU program, with the other half will be provided by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the Ministry of Culture and Science of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia (MKW NRW), where the Forschungszentrum Jülich is sited.
Jupiter will be based on a dynamic, modular supercomputing architecture, which has already been used for the Juwels supercomputer. This apparently allowed the Juwels system to be upgraded in 2020 so that the CPU-based cluster module was joined with a booster module equipped with GPUs. Both modules were based on Atos BullSequana X hardware.
With Jupiter, the basic configuration will include a universal cluster module and GPU accelerators, plus a high capacity parallel storage module, high bandwidth flash storage, and a high capacity backup and archive setup.
Optional units in the configuration are another GPU booster and an interactive computation and visualization module, while future modules could include a quantum processing unit and a neuromorphic processing module.
Jupiter has also apparently been designed as a "green" supercomputer and will be powered by green energy, according to the Forschungszentrum Jülich. It is also expected that Jupiter's cooling system will be connected to the new low-temperature network on the campus so that the waste heat generated can be reused.
If this sounds familiar, it is because the LUMI supercomputer announced by EuroHPC earlier this week in Finland is also powered using green energy and uses the waste heat it generates to contribute towards heating nearby homes.
The final decision to locate Europe's first exascale computer at the Forschungszentrum Jülich was apparently made during the inauguration of the LUMI system.
Exact specifications for Jupiter have not been disclosed, but both the Frontier exascale system and LUMI have been built with HPE Cray EX hardware, using AMD Epyc CPUs and MI250X GPU accelerators, with nodes linked using the HPE Slingshot interconnect.
Forschungszentrum Jülich is also becoming something of a supercomputing hub, as it has been home since March to Germany's QSolid project which aims to develop a complete quantum computer system using home-grown technology. ®
Looking for more? Now read an analysis of this news on The Next Platform.
Netzwerkkabel verlegen: Infos und Anleitung
Neben der reinen Übertragungsgeschwindigkeit beziehungsweise -frequenz gibt es noch weitere Kriterien, die Sie beim Kabelkauf ebenfalls nicht außer Acht lassen sollten:
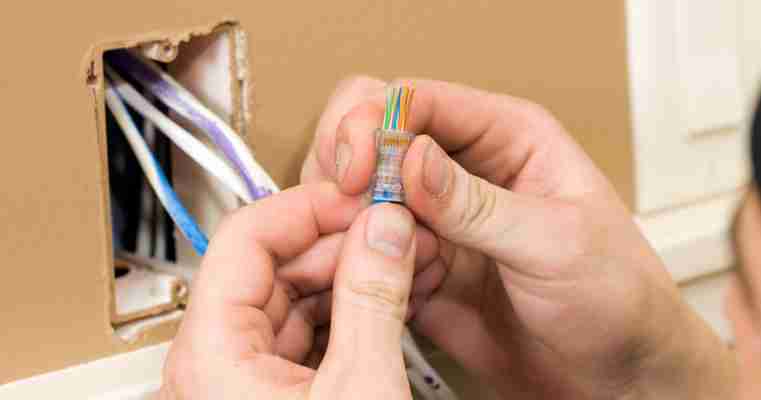
Abschirmung: Die Stabilität Ihres Hausnetzwerkes kann durch elektromagnetische Felder erheblich geschwächt werden. Deshalb sollten Sie auf eine möglichst gute Schirmung der LAN-Kabel achten, vor allem wenn Sie die Netzwerkkabel in Leitungsschächten neben Stromkabeln oder anderen elektrischen Leitungen verlegen. Beim Kauf geben die Buchstaben hinter der Frequenz Auskunft über die Abschirmung des Kabels (zum Beispiel CAT 6 500 MHz F/STP).
Ein Überblick über die geläufigen Buchstabenkombinationen:
U: Das Kabel ist nicht abgeschirmt. F: Das Kabel ist mit einer metallisierten Folie abgeschirmt. S: Das Kabel ist mit einem Kupfergeflecht abgeschirmt. SF: Das Kabel ist sowohl geflecht- als auch folienabgeschirmt. XX: Das gesamte Kabel ist umschirmt. Y: Die einzelnen Aderpaare sind separat abgeschirmt. TP: Die Aderpaare sind verdrillt.
Beispiel: Bei einem Kabel mit der Bezeichnung F/STP sind also alle Kabel mit einer Folie umschirmt, zusätzlich werden die einzelnen verdrillten Aderpaare mit einem Kupfergeflecht geschützt.
LAN Verkabelung Neubau
Vorab: Was ist ein CAT Kabel?
Bei CAT Kabeln handelt es sich um Ethernet-Patchkabel. Es sind Netzwerkkabel. Man spricht auch von LAN Kabeln oder Twisted-Pair-Kabeln. Sie werden für die Ethernet Übertragung benötigt und bestimmen die Abschirmungsqualität.
Welche Verkabelung im Neubau?
Wählen Sie für Ihren Neubau eine zukunftssichere LAN-Verkabelung. Das Ethernet in der Ausführung Twisted-Pair (verdrilltes Adernpaar) ist der aktuelle Standard. Setzen Sie dabei auf eine hochwertige Abschirmungsqualität. Die Qualität erkennen Sie an der Kategorie. Im Heimbereich benötigen Sie mindestens CAT 5E.
Welches Kabel für LAN im Haus?
Verlegen Sie das LAN-Kabel im Eigenheim immer sternförmig und am besten in einem Leerrohr. Aktuell sind sehr häufig CAT 7 Kabel und CAT 6a Netzwerkdosen im Einsatz. (Stand: Oktober 2020)
Kann man Netzwerkkabel verteilen?
Sie können ein LAN-Kabel mit Hilfe eines kleinen, separaten Gerätes splitten. Durch einen solchen Adapter können Sie weitere Netzwerkkabel für Ihre optimale LAN Verkabelung anschließen. Dafür benötigen Sie eine Switch oder einen Hub.
